There is a ton of information on the web about marijuana and the biology of Cannabis.
There is a ton of information on the web about marijuana and the biology of Cannabis.
However, the following (5) facts about marijunana below are some of the most interesting in our opinion, and demonstrate that there is much to learn and admire about this wonderful plant.
In no particular order, here they are:
1) THC Likely Evolved as a Plant Defense.
Given all of the emerging research about marijuana’s various positive health and body effects for humans, it’s easy to forget that its psychoactive arsenal was intended originally to benefit the plant itself.
Specifically, it’s believed that the cannabinoids the plant produces, including Tetrahydrocannabinol (“THC”), actually evolved to protect the Cannabis plant in the following ways:
- Preventing Dessication. THC is a hydrophobic (water-repelling) oil that helps keep marijuana plants from drying out in dry climates by creating an impervious layer over the leaf, much like the waxy cuticles of desert-adapted plants, such as cacti and other succulents. And comparisons between wild cannabis populations generally support this, showing that plants lving in drier, more xeric conditions with low rainfall and humidity produce substantially more THC than than plants growing in wetter, more hospitable climes.
 Defending Against Insect Predation. The presence of very small stiff hairs (i.e., trichomes) on a marijuana plant’s leaves, which can become laced with a sticky, volatile cannabinoid exudate (especially flowering plants) are believed to help thwart insect damage in a couple of ways. First, the pungent aroma of this sap-like substance smells strongly of terpenes (an aromatic hydrocarbon), which are believed to harbor insect-repelling properties. This is consistent with studies that have shown THC to repel or outright kill some agricultural pests. Secondly, the sheer stickiness of THC resin may minimize insect damage by gumming up larger insects’ mouthparts and ensnaring smaller sap-sucking insects entirely.
Defending Against Insect Predation. The presence of very small stiff hairs (i.e., trichomes) on a marijuana plant’s leaves, which can become laced with a sticky, volatile cannabinoid exudate (especially flowering plants) are believed to help thwart insect damage in a couple of ways. First, the pungent aroma of this sap-like substance smells strongly of terpenes (an aromatic hydrocarbon), which are believed to harbor insect-repelling properties. This is consistent with studies that have shown THC to repel or outright kill some agricultural pests. Secondly, the sheer stickiness of THC resin may minimize insect damage by gumming up larger insects’ mouthparts and ensnaring smaller sap-sucking insects entirely.- Inhibiting Microbial/Fungal Growth. Marijuana has long been known to have antiseptic properities; the chemical structure and effect of one cannabanoid, cannabigerol (“CBG”), has been found analogous to the antibacterial compounds produced by the fungi Grifolia conflens.
- Shielding Harmful UV-B Radiation. While light is vital for promoting growth, high levels of its UV-B component can quickly destroy plant tissues and impede growth. In regions receiving high levels of ultraviolet radiation, the spectral absorptive range of THC (which is approximately 280 to 315 nm) provides Cannabis protection from UV-B, much like the pigment melanin does for human skin. In fact, experiments show that production of THC actually increases in plants subjected to high levels of UV-B light.
2) Marijuana Use is Truly Ancient.

The Chinese character for hemp.
You may know that weed has been around for a long time, but just how long might surprise you.
The earliest written records of medical Cannabis use are from Asia, where the plant is believed to have originated.
The first documented use for medicinal purposes come from central China in the year 2727 BC. India and Nepal were not far behind, with religious texts dated between 2000 to 1400 BC that identify Cannabis as a “sacred plant” possessing powerful spiritual and medicinal powers.
Northern Europeans didn’t get wind of weed until around 500 BC. But once they did it spread quickly.
In fact, by 170 AD, Cannibis was being used by the Romans medicinally, and the evidence suggests that the Romans were also “on to” hemp’s curious “psychoactive” properties as well.
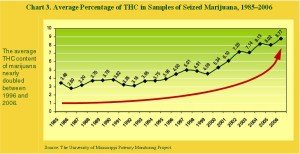
3) Medicinal Cannabis Potency Has Doubled Over the Past 20 Years.
Some of most impressive data showing the steady rise in THC content over the past two decades comes from the University of Mississippi Potency Monitoring Project. This team tracked the average THC content from seized batches of Cannabis between 1985 and 2006 and found that the concentration of THC nearly doubled within this 20-year span, with the final year of the study recording the most potent weed of all (8.8% THC compared to 3.5% THC in 85′).
However, these data may be an underestimate just how fast THC content is actually rising, as more recent reports put the THC content for seized cannabis at well over 10%, with the average THC content in coffee shop Cannabis in the Netherlands estimated to range between roughly 18 to 19%!
So how and why is this happening?
According to the National Drug Threat Assessment (2008), this dramatic rise in potency is largely attributable to “improved and highly efficient outdoor and indoor cultivation methods,” such as the use of “cloned plants” and “high nutrient fertilizers.”
4) Shakespeare Was Likely a “Toker.”
 With its psychoactive properties, it’s no surprise that modern artists are likely to find inspiration by availing themselves of some occasional Cannabis.
With its psychoactive properties, it’s no surprise that modern artists are likely to find inspiration by availing themselves of some occasional Cannabis.
But you may be surprised to learn that good old William Shakespeare himself apparently owed some of his creative juices to a bit of weed as well.
It’s no joke.
A South African Journal reports that pipes unearthed from the garden area around Shakespeare’s Stratford-upon-Avon home revealed trace amounts of marijuana.
This, according to the researchs, may explain the basis for certain passages in some of Shakespeare’s works, such as the “noted weed” referenced in Sonnet 76, and the “journey in my head” in Shakespeare’s Sonnet 27.
5) Marijuana May Not Cause And Could In Fact Inhibit Lung Cancer.
We saved the best for last. When the prominent cancer researcher, Donald Tashkin, of the University of California in Los Angeles began a cancer study of over a thousand subjects, over half of which had cancers in the lung, head and neck, he believed he would find linkage between the incidence of cancer and heavy marijuana smoking.
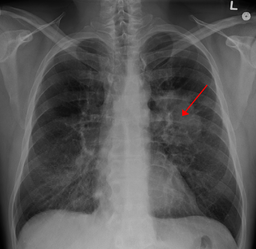 However, on the contrary, and after carefully controlling for the potentially confounding factors of age, gender, neighborhood and other drug use, no connection was discovered. In fact, even those users who smoked over 20,000 joints did not have any higher cancer risk.
However, on the contrary, and after carefully controlling for the potentially confounding factors of age, gender, neighborhood and other drug use, no connection was discovered. In fact, even those users who smoked over 20,000 joints did not have any higher cancer risk.
This finding was more than unexpected, it surprised Tashkin, particularly since smoking joints would seem to be more dangerous than cigarettes: “Marijuana is packed more loosely than tobacco, so there’s less filtration…so more particles will be inhaled.” In addition, Tashkin added, marijuana smokers “hold their breath about four times longer [than tobacco smokers] allowing more time for extra fine particles to deposit in the lungs.”
So why no cancer link, especially given this greater contact between the smoke and lungs? Tashkin theorizes that THC may harbor a compound that causes older cells to die before they have the chance to turn into cancers – read more about marijuana’s potentially anti-cancer benefits.
Any More Facts You’d Care to Share?
To be honest, I realize there are way more than just 5 interesting things about marijuana. Do you have some interesting facts about marijuana that you’d like to share? We would love to hear from you!
Article Source(s):
http://www.hempfood.com/IHA/iha01201.html
http://www.justice.gov/archive/ndic/pubs25/25921/25921p.pdf
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Religious_and_spiritual_use_of_cannabis#cite_note-2
http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/programmes/panorama/4079668.stm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabis_%28drug%29#cite_note-Leonard2009-50
http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/large-study-finds-no-link/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabis_%28drug%29#cite_note-Calabria2010-37
Image Source(s):
Cannabis Training University (Own work) under CC-BY-SA-3.0
Cannabis_female_flowers under CC-BY-SA-3.0
Michaeltb under CC-BY-3.0
John Taylor (painting) public domain
By James Heilman, MD under CC-BY-SA-3.0